If you are sitting for the 2025 WAEC Agricultural Science Practical exam, this guide is for you. WAEC has released the full list of specimens that will be used during the exam. As a student, you need to know each specimen well — what it is, how it is used in farming, and how to describe it properly during your practical.
Each candidate will be given some real-life farm tools, samples of fertilizers and manures, insect pests, and some animal body parts. All these are meant to test how much you understand about crop production, pest control, farm tools, and animal husbandry.
Below is the list of specimens provided for the 2025 Agricultural Science Practical:
- A: Ammonium sulphate (labelled)
- B: Muriate of potash (labelled)
- C: Cow dung
- D: Compost (labelled)
- E: Cutlass
- F: Spade
- G: Wheelbarrow
- H: Yam beetle
- I: Cowpea weevil
- J: Centrosema pubescens
- K: Spear grass
- L: Gizzard (chicken)
- M: Goat skin (fresh, with hairs intact)
- N: Horn
In this article, we will explain each specimen one by one using simple language. You’ll also get hints on the likely questions WAEC may ask you during the exam.
Let’s begin with Specimen A: Ammonium sulphate (labelled).
Specimen A: Ammonium Sulphate (Labelled)
Ammonium sulphate is a type of chemical fertilizer. It is often used by farmers to help crops grow better. This fertilizer provides nitrogen, which is an important nutrient that helps plants grow strong and green.

Key Features to Observe:
- It looks like white or light grey crystals or granules
- It is usually dry and may feel a bit powdery
- It is stored in a labeled bag or container
Importance in Agriculture:
Ammonium sulphate is a nitrogen-based fertilizer, and nitrogen helps plants grow leaves and stems. Farmers often use it for crops like maize, rice, and vegetables.
What You Should Know:
- It is used before or during planting
- It should be applied in the soil, not on the leaves
- Overuse can harm the soil or the plant
Likely Exam Questions:
- Identify the specimen and state its use
- Name the major nutrient it supplies to plants
- Mention one advantage and one disadvantage of using chemical fertilizers
Specimen B: Muriate of Potash (Labelled)
Muriate of potash, also known as potassium chloride, is another type of chemical fertilizer. This one gives the plant potassium, which helps in the formation of healthy fruits and strong roots.

Key Features to Observe:
- It appears as white or pinkish crystals or granules
- It may feel dry and a bit rough
- It is packed in a container with a label for identification
Importance in Agriculture:
Potassium is one of the three main nutrients plants need — the others are nitrogen and phosphorus. Muriate of potash helps:
- Improve fruit quality
- Strengthen plant resistance to diseases
- Promote root development
What You Should Know:
- It is best used on root crops and fruiting crops
- It should be mixed into the soil, not sprinkled on the leaves
- It works well when used with other fertilizers like ammonium sulphate
Likely Exam Questions:
- Identify the specimen and state the major nutrient it provides
- Mention two crops that benefit from potassium
- Compare it with ammonium sulphate in terms of nutrient content
Specimen C: Cow Dung
Cow dung is the waste (faeces) from cows. It is a type of organic manure because it comes from a living animal. Farmers use it to improve soil quality and help crops grow naturally without chemicals.

Key Features to Observe:
- It looks dark brown or black, sometimes sticky or dry
- It has a strong smell
- It may be seen in clumps or already dried for use
Importance in Agriculture:
Cow dung is rich in nutrients that help plants grow. It also improves the texture of the soil, making it easier for roots to spread and water to soak in.
What You Should Know:
- It is usually added to the soil before planting
- It works slowly but improves the soil over time
- It is safer for the environment compared to chemical fertilizers
Likely Exam Questions:
- Identify the specimen and state its type
- Mention two nutrients found in cow dung
- List two advantages of using organic manure
Specimen D: Compost (Labelled)

Compost is a type of organic manure made by rotting plant and animal materials, like leaves, food waste, paper, and even animal droppings. It is rich in nutrients and helps to improve soil fertility naturally.
Key Features to Observe:
- It looks like dark brown or black soil
- Has a slightly earthy smell
- Soft and crumbly when touched
- It may contain small, broken pieces of dry leaves or other natural matter
Importance in Agriculture:
Compost adds nutrients to the soil and makes it better for planting. It also helps the soil hold more water and air, which is good for healthy root growth.
What You Should Know:
- Compost is environment-friendly
- It improves soil structure and drainage
- It can be made easily on farms or at home using waste materials
Likely Exam Questions:
- Identify the specimen and describe its appearance
- Mention two materials used to make compost
- State two benefits of compost to the soil
Specimen E: Cutlass
The cutlass is a common farm tool used by farmers, especially in West Africa. It is used for clearing bushes, cutting weeds, and harvesting crops. It looks like a long metal blade with a handle, and it can be straight or slightly curved.

Key Features to Observe:
- A metal blade (shiny or dark, sometimes rusted)
- A wooden or plastic handle
- May be straight or curved at the tip
- Light enough to carry and swing with one hand
Importance in Agriculture:
The cutlass is one of the most widely used tools on the farm. It is used for:
- Clearing grass and weeds
- Harvesting crops like yam or cassava
- Cutting small branches or shrubs
What You Should Know:
- It should be kept sharp and clean
- It must be handled carefully to avoid injury
- It is best used for light farm work, not digging
Likely Exam Questions:
- Identify the specimen and state two uses
- Mention two maintenance practices for a cutlass
- List one advantage and one disadvantage of using a cutlass
Specimen F: Spade

A spade is a farm tool used mainly for digging, lifting, and turning soil. It has a flat metal blade and a strong handle, making it useful for preparing the land before planting.
Key Features to Observe:
- A broad, flat blade made of metal
- A long handle, usually made of wood or metal
- The edge of the blade is straight, not sharp like a cutlass
- It may have a small step at the top of the blade to help with foot pressure
Importance in Agriculture:
The spade helps farmers and gardeners do heavy soil work. It is used for:
- Digging holes or trenches
- Turning and loosening soil
- Lifting soil, compost, or manure
- Transplanting seedlings
What You Should Know:
- The spade is more suitable for heavy-duty work than a cutlass
- It should be kept clean and dry to avoid rust
- It must be used with proper posture to avoid injury
Likely Exam Questions:
- Identify the specimen and describe its use
- Compare the spade with a cutlass
- Mention two ways to maintain a spade
Specimen G: Wheelbarrow
A wheelbarrow is a one-wheeled cart used on the farm to carry heavy loads like manure, harvested crops, soil, or tools. It has a big open container, one front wheel, and two handles at the back for pushing.

Key Features to Observe:
- A large metal or plastic tray (where items are placed)
- One wheel in front for movement
- Two handles for holding and pushing
- May have two supporting legs at the back to keep it steady when not in use
Importance in Agriculture:
The wheelbarrow helps farmers transport things easily around the farm without carrying them by hand. It is very useful during:
- Land preparation
- Harvesting
- Applying manure or compost
- Clearing farm waste
What You Should Know:
- It saves time and reduces physical stress
- It should not be overloaded to avoid damage or accidents
- Keep the wheel pumped and tray clean for long-lasting use
Likely Exam Questions:
- Identify the specimen and state two uses
- Mention two maintenance practices for a wheelbarrow
- State one advantage of using a wheelbarrow on the farm
Specimen H: Yam Beetle
The yam beetle is a pest that attacks yam crops, especially while the yam is still growing in the soil. It feeds on the tubers, causing holes and damage that reduce the quality and quantity of the harvest.

Key Features to Observe:
- It is a hard-bodied insect, often black or dark brown
- The body is shiny and oval-shaped
- Has six legs, antennae, and strong jaws for biting into yam
- May be seen alive or preserved in a container during the exam
Importance in Agriculture:
Yam beetles are harmful because:
- They bore into yam tubers, making them rot easily
- They reduce the size and weight of harvested yams
- Damaged yams sell for less money in the market
What You Should Know:
- The beetle is found in yam-growing areas
- It lives mostly in the soil
- Farmers control it using chemicals, early harvesting, or crop rotation
Likely Exam Questions:
- Identify the specimen and state the crop it attacks
- Describe one way the pest causes damage
- Mention two methods of controlling yam beetles
Specimen I: Cowpea Weevil
The cowpea weevil is a small insect pest that attacks cowpea seeds (also known as beans). It is often found in stored beans and causes damage by boring holes and feeding on the inside of the seeds.

Key Features to Observe:
- Small-sized insect, usually brown or black
- Oval or round body with a hard outer shell
- Has six legs and short antennae
- Often found with damaged or holed beans
Importance in Agriculture:
The cowpea weevil is a serious storage pest. It destroys seeds after harvest, especially during storage. This leads to:
- Loss of food and poor seed quality
- Weight loss in stored beans
- Lower market value of the product
What You Should Know:
- The pest lays eggs on beans, and the young ones (larvae) eat the beans from inside
- Can be controlled using airtight containers, drying the beans well, or natural insect repellents
Likely Exam Questions:
- Identify the specimen and name the crop it attacks
- Describe one sign of damage caused by this pest
- State two ways to control cowpea weevils during storage
Specimen J: Centrosema pubescens
Centrosema pubescens is a type of leguminous plant often used for soil improvement and animal feed. It is a climbing or creeping plant that grows mostly in tropical areas and is known for fixing nitrogen into the soil.

Key Features to Observe:
- Green leaves, usually in threes (trifoliate)
- Purple or bluish flowers (may or may not be seen during the exam)
- Soft stems that can trail along the ground or climb other plants
- May have fine hairs on the leaves or stem (as the name “pubescens” means hairy)
Importance in Agriculture:
- It is used as a cover crop to protect soil from erosion
- It helps to add nitrogen to the soil, improving fertility
- Farmers also use it as forage for animals (like goats and cows)
What You Should Know:
- It is one of the natural ways to improve soil without using chemical fertilizers
- Helps in weed control by covering the ground
- Grows well in hot, moist environments
Likely Exam Questions:
- Identify the plant and state one of its uses
- Mention the type of root nodules it has
- Explain how it improves soil fertility
Specimen K: Spear Grass
Spear grass is a tough, weedy grass that grows in many farmlands, especially in West Africa. It is known for its sharp, pointed leaves that can cut the skin and make farm work difficult. Farmers often see it as a weed because it competes with crops for space, water, and nutrients.

Key Features to Observe:
- Long, narrow leaves with sharp edges
- Pointed tips that feel like a spear or blade
- Leaves may feel rough or stiff
- It spreads easily and can form thick bushes if not controlled
Importance in Agriculture:
Spear grass is not useful to crops — it is mostly a nuisance on farms. It:
- Competes with crops for nutrients
- Reduces crop yield
- Makes clearing land more stressful for farmers
What You Should Know:
- It grows quickly and spreads fast
- Difficult to remove completely because of its strong roots
- Best controlled by early weeding, slashing, or herbicides
Likely Exam Questions:
- Identify the specimen and state whether it is useful or a weed
- Describe one effect of spear grass on crops
- Mention two methods used to control it on the farm
Specimen L: Gizzard (Chicken)
The gizzard is a part of a chicken’s digestive system. It is a thick, muscular organ found in the lower part of the digestive tract. Chickens use the gizzard to grind and crush food, especially grains, since they don’t have teeth.
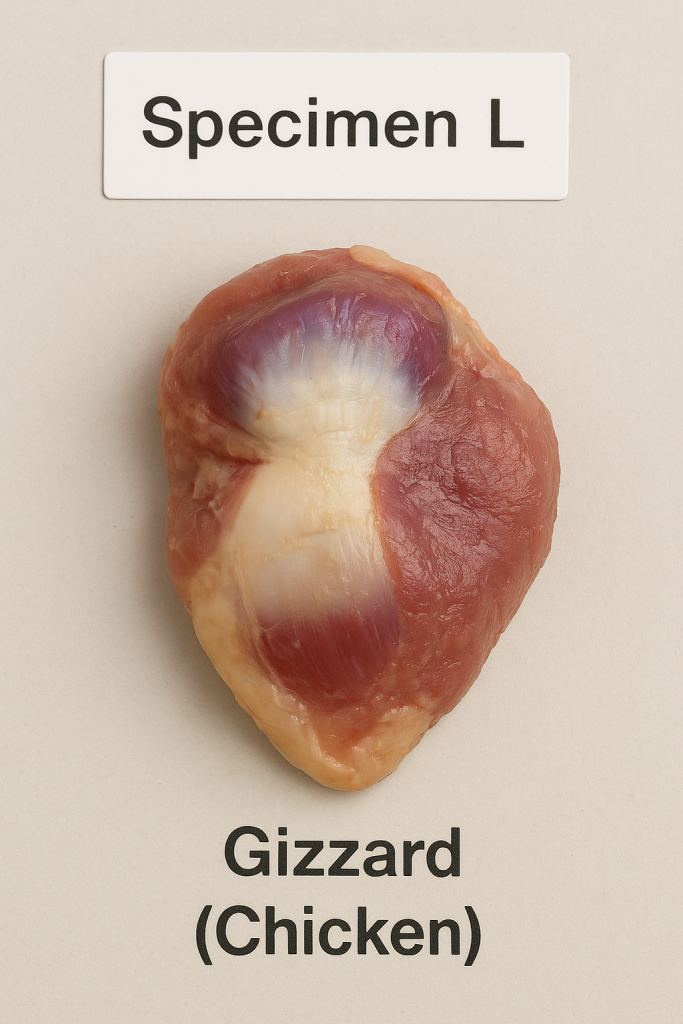
Key Features to Observe:
- It looks round or oval, and thick-walled
- The inside is rough and muscular
- It may still have some food particles or small stones inside
- Usually dark red or grey in color
Importance in Agriculture:
The gizzard helps in digesting food in birds. Farmers who rear poultry need to understand the parts of the chicken for proper feeding and health care.
What You Should Know:
- Chickens swallow small stones (called grit) that help the gizzard grind food
- The gizzard is very strong and works like a grinder
- It is different from the stomach in humans
Likely Exam Questions:
- Identify the specimen and state its function
- Describe the structure of the gizzard
- Explain how chickens digest food without teeth
Specimen M: Goat Skin (Fresh, with Hairs Intact)
This is the outer covering (skin) of a goat that has been freshly removed, with the hairs still on it. It is used to study the body covering of farm animals and to understand the uses of animal skin in agriculture.

Key Features to Observe:
- It is soft and flexible, since it is fresh
- Still has goat hair on it
- May have a natural smell (if not preserved)
- The color may be brown, black, or white, depending on the goat breed
Importance in Agriculture:
- It teaches about animal products that can be used by humans
- Goat skin can be used for making leather and traditional items
- The hair helps to protect the goat from cold and heat
What You Should Know:
- Skin is one of the by-products of livestock
- It is useful in both farming and industries (leather production)
- Proper handling is needed to preserve it from decay
Likely Exam Questions:
- Identify the specimen and mention its source
- State two uses of goat skin
- Describe the function of skin to animals
Specimen N: Horn
The horn is a hard, pointed structure that grows on the head of some animals, like goats, cattle, and rams. It is made of a material called keratin, the same substance found in human nails and hair. In Agriculture, horns help identify animal breeds and are considered a by-product of livestock.

Key Features to Observe:
- Hard and curved in shape
- Usually black, brown, or grey
- Has a pointed tip and a wider base
- May feel smooth or slightly rough
Importance in Agriculture:
- Horns are used for defense and fighting among animals
- Farmers may trim or remove horns to prevent injury in the pen
- Horns can also be used to identify the age or breed of livestock
- In some cultures, horns are used to make decorations or tools
What You Should Know:
- Not all animals have horns — some are naturally polled (hornless)
- Horns do not grow back once removed
- Care is needed when handling animals with horns
Likely Exam Questions:
- Identify the specimen and mention the animal it comes from
- State one function of horns in animals
- Mention one reason why farmers remove animal horns
Final Summary for WAEC Agricultural Science Practical 2025
The 2025 WAEC Agricultural Science Practical exam will include a mix of fertilizers, organic manures, farm tools, insect pests, useful and harmful plants, and animal parts. These specimens are meant to test your understanding of real-life agricultural practices.
Here’s a quick recap of the specimen types:
- A–D: Types of fertilizers and manures
- E–G: Common farm tools
- H–I: Pests that damage crops
- J–K: Useful and harmful plants
- L–N: Animal parts and by-products
You should be able to:
- Identify each specimen
- Describe its function or use in farming
- Mention its advantages or disadvantages
- Suggest control methods for pests or care tips for tools and animals
Important Notes for Schools and Candidates
WAEC has also provided instructions on how to prepare for the practical:
(a) Specimen Handling:
- Each candidate must receive well-labeled specimens (e.g., A, B, C… N).
- Real specimens should be provided. Pictures or diagrams are not allowed unless listed as official specimens.
(b) Items to be Provided for Each Candidate:
To perform well in the practical, each candidate must be given the following tools and materials:
- A hand lens (magnifying glass)
- Beaker
- Plastic syringe (without needle)
- Sodium hydroxide (chemical for testing)
- 1% copper sulphate solution
- Scalpel (for cutting specimens)
- Test tube
- Test tube rack
- Bunsen burner (for heating if required)
These tools will help you carry out basic experiments, examine specimens more closely, and answer questions correctly.

