If you are writing NECO Biology Practical in 2025, this article is very important for you. The National Examinations Council (NECO) has officially released the list of specimens that students will be using during the practical exam. Knowing these early gives you time to prepare well before the exam day.
Let’s go through everything you need to know, step by step, in clear and simple words.
What Is the NECO Biology Practical Exam About?
The Biology Practical exam is a hands-on test where you will observe, draw, and write about real-life specimens (plants, animals, seeds, fruits, bones, etc.). It is different from the normal theory exam because here, you are tested based on what you can see and explain from experience, not just from textbooks.
You will also be asked to draw and label specimens, answer questions based on their features, functions, and classifications. So, it is important to get familiar with them before the exam.
Important Warning from NECO
NECO clearly stated that the information about the Biology Practical exam is highly confidential. This means it must not be shared carelessly or discussed with students before the exam day. It is meant to help teachers and schools prepare the materials on time.
So if you are a student reading this, please use it wisely to study and prepare. Don’t misuse it or spread it around to others in a way that breaks NECO rules.
What Should Each Student Bring to the Exam Hall?
NECO has listed some basic tools that every student must bring along on the day of the Biology Practical exam. These are:
- A well-sharpened HB drawing pencil (not B or 2B)
- A clean eraser (to correct mistakes in your diagrams)
- A ruler (for straight lines when labeling)
These small tools are very important. If you forget them, it may affect your performance, especially in questions that involve drawing and labeling.
What the School Must Provide for the Students
Apart from what students must bring, the school also has a duty to provide some materials that will be used by all candidates during the exam. These include:
- A sharp razor blade or a scalpel (used to cut specimens neatly)
- A petri dish (to hold small specimens)
- A hand lens (a small magnifying glass used to observe fine details of the specimen)
The school should make sure these materials are in good condition and available before the exam starts.
Full List of NECO Biology Specimens for 2025
These are the specimens NECO has released for the 2025 Biology Practical. Students will be expected to observe them, answer questions, and possibly draw some of them:
- A – Housefly
- B – Spider
- C – Pride of Barbados Flower
- D – Bean Seed
- E – Butterfly
- F – Crayfish
- G – Grasshopper
- H – Humerus of a Rabbit
- I – Femur of a Rabbit
- J – Orange Fruit
- K – Honey Bee
- L – Land Snail
- M – Guava Fruit
- N – Irish Potato Tuber
- O – Sweet Potato Tuber

Specimen A – Housefly
The housefly is a small insect commonly found around homes and dirty areas. It has two wings, compound eyes, and six legs. Houseflies are known for spreading diseases because they carry germs from dirty places to food.
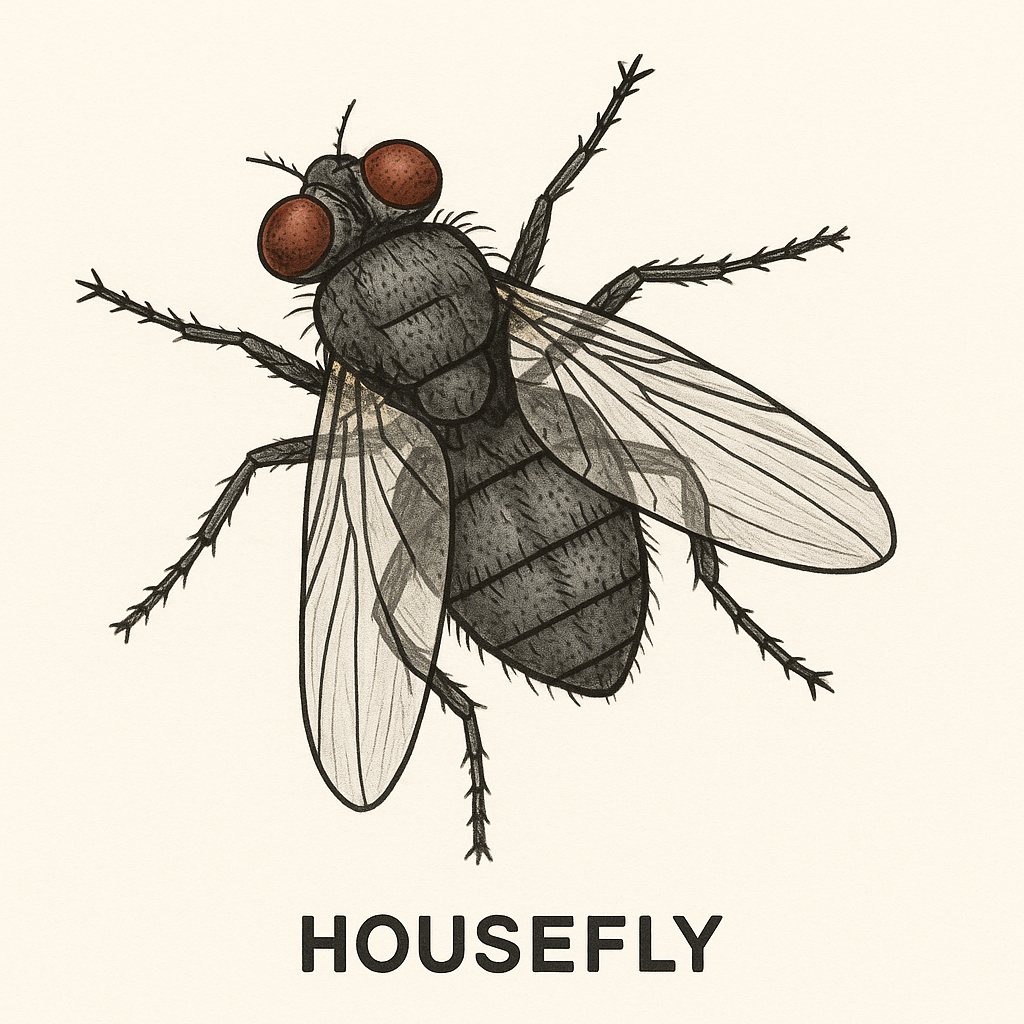

Key features:
- Belongs to the insect group
- Has a soft body and can fly
- Lays eggs on decaying matter
Use in Biology Practical: You may be asked to describe its body parts (head, thorax, abdomen), how it feeds, or its role in disease transmission.
Specimen B – Spider
Spiders are arachnids, not insects. They have eight legs, unlike insects that have six. Spiders do not have wings. They build webs to catch insects and are useful in controlling pests.
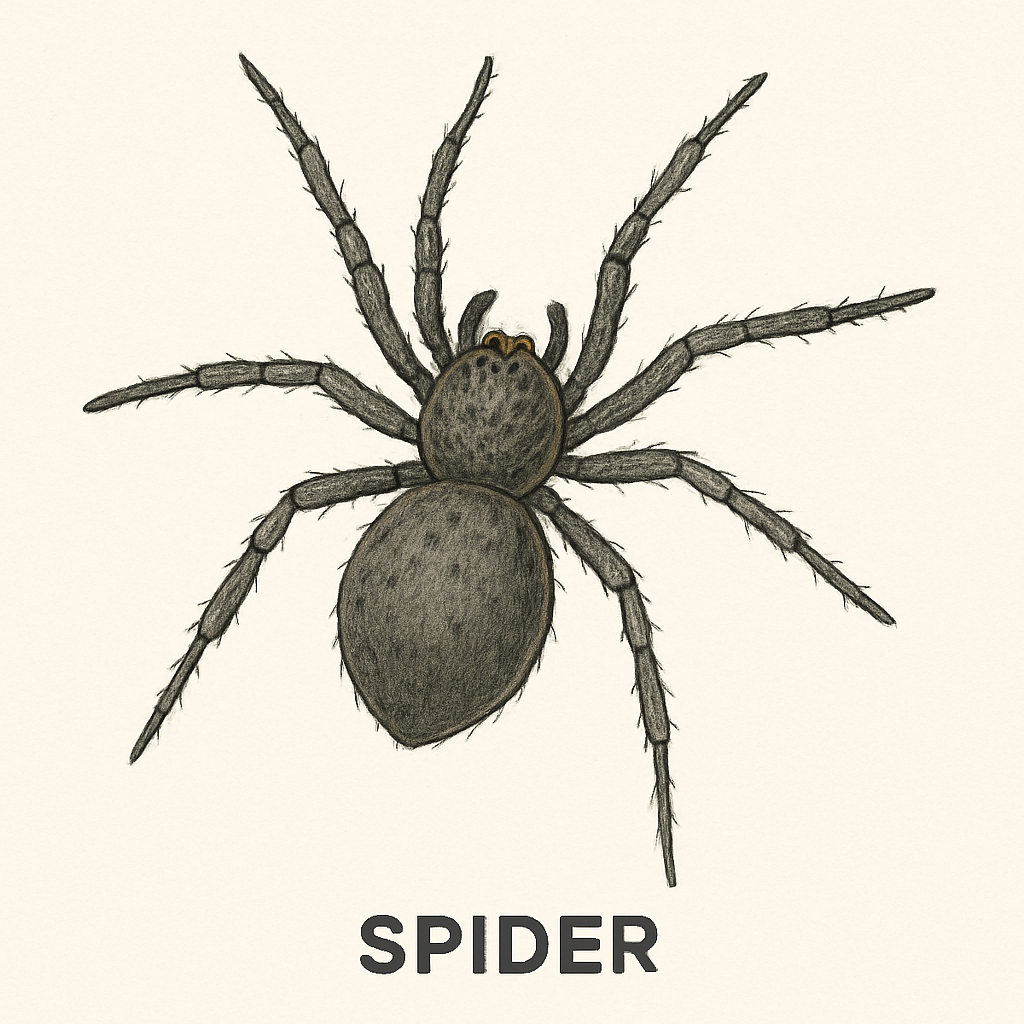

Key features:
- Has two main body parts (cephalothorax and abdomen)
- Eight simple eyes
- Produces silk from spinnerets
Use in Biology Practical: You may be asked to identify the spider’s body parts and explain the difference between spiders and insects.
Specimen C – Pride of Barbados Flower
This is a bright-colored flowering plant with red, orange, or yellow petals. It is used for decoration and has stamens and pistils that are visible, making it good for studying flower parts.

Key features:
- Has both male and female parts (a complete flower)
- Shows clear reproductive parts
- Has colorful petals to attract pollinators
Use in Biology Practical: You may be asked to label parts of the flower and explain their functions (e.g., stamen for pollen, pistil for ovules).
Specimen D – Bean Seed
The bean seed is a dicotyledonous seed, which means it has two seed leaves (cotyledons). It stores food for the baby plant during germination.

Key features:
- Has seed coat (testa)
- Has hilum (the scar where it was attached to the pod)
- Contains an embryo with a radicle and plumule
Use in Biology Practical: You may be asked to identify the parts of the seed and explain how it germinates.
Specimen E – Butterfly
Butterflies are colorful insects known for their beautiful wings. They go through a life cycle called metamorphosis (egg → larva → pupa → adult).
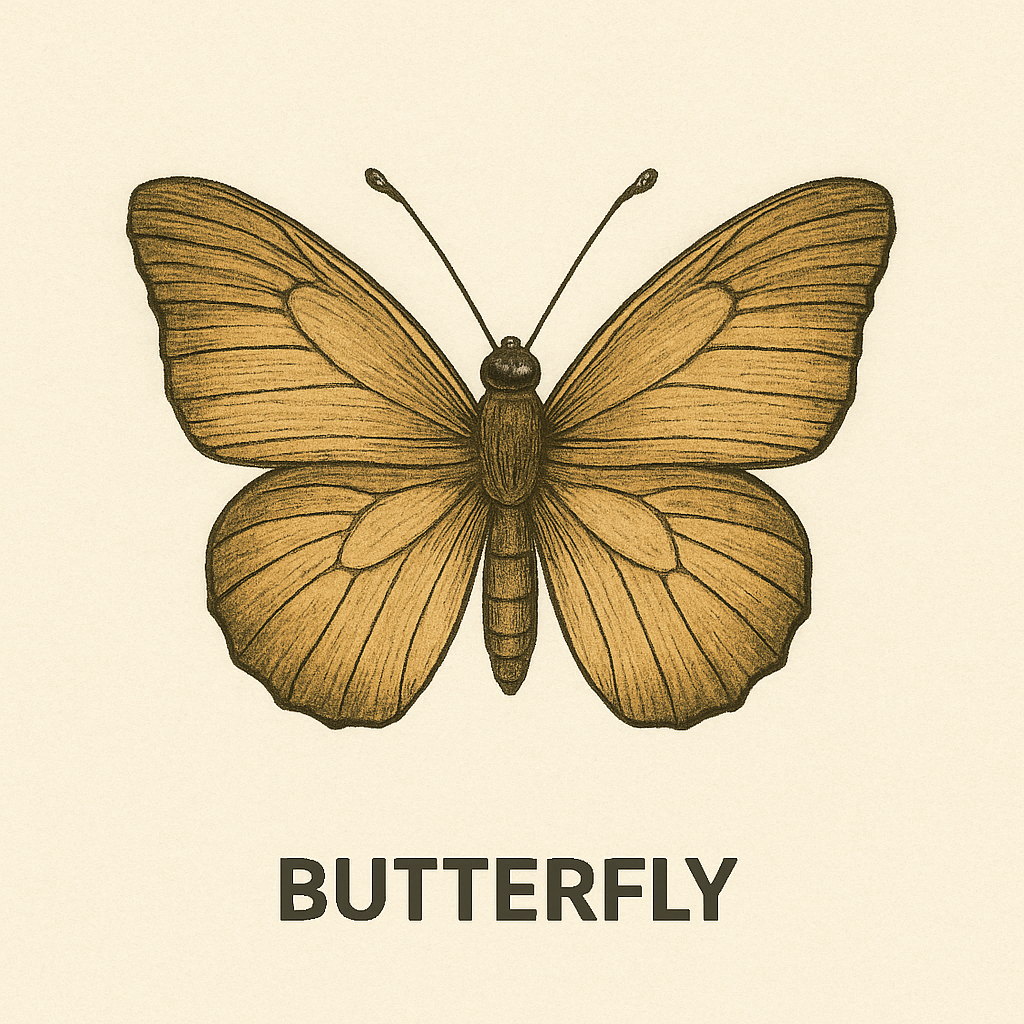

Key features:
- Four large wings covered with scales
- Long coiled proboscis for sucking nectar
- Six legs and compound eyes
Use in Biology Practical: You may be asked to label the butterfly, describe its life cycle, or compare it to other insects.
Specimen F – Crayfish
Crayfish are aquatic animals that look like small lobsters. They live in water and use gills to breathe.

Key features:
- Hard outer shell (exoskeleton)
- Five pairs of legs (first pair has pincers)
- Two antennae and compound eyes
Use in Biology Practical: You may be asked to draw and label the external parts or describe how it breathes and moves.
Specimen G – Grasshopper
Grasshoppers are jumping insects with strong back legs. They live on land and feed on plants.

Key features:
- Three body parts (head, thorax, abdomen)
- Two pairs of wings
- Powerful hind legs for jumping
Use in Biology Practical: You may be asked to label parts and explain how they move or the type of mouthparts they have.
Specimen H – Humerus of a Rabbit
The humerus is the upper arm bone of the rabbit. It connects the shoulder to the lower arm.

Key features:
- Long bone
- Has a rounded head for joint movement
- Supports muscle attachment
Use in Biology Practical: You may be asked to identify the bone and its function or compare it to other long bones.
Specimen I – Femur of a Rabbit
The femur is the thigh bone and the longest bone in a rabbit’s body. It supports movement and carries weight.

Key features:
- Thick and strong
- Joins with the hip at the top and knee at the bottom
- Contains bone marrow inside
Use in Biology Practical: You may be asked to compare the femur to the humerus or describe its role in movement.
Specimen J – Orange Fruit
Orange is a juicy fruit rich in Vitamin C. It is an example of a fleshy fruit.
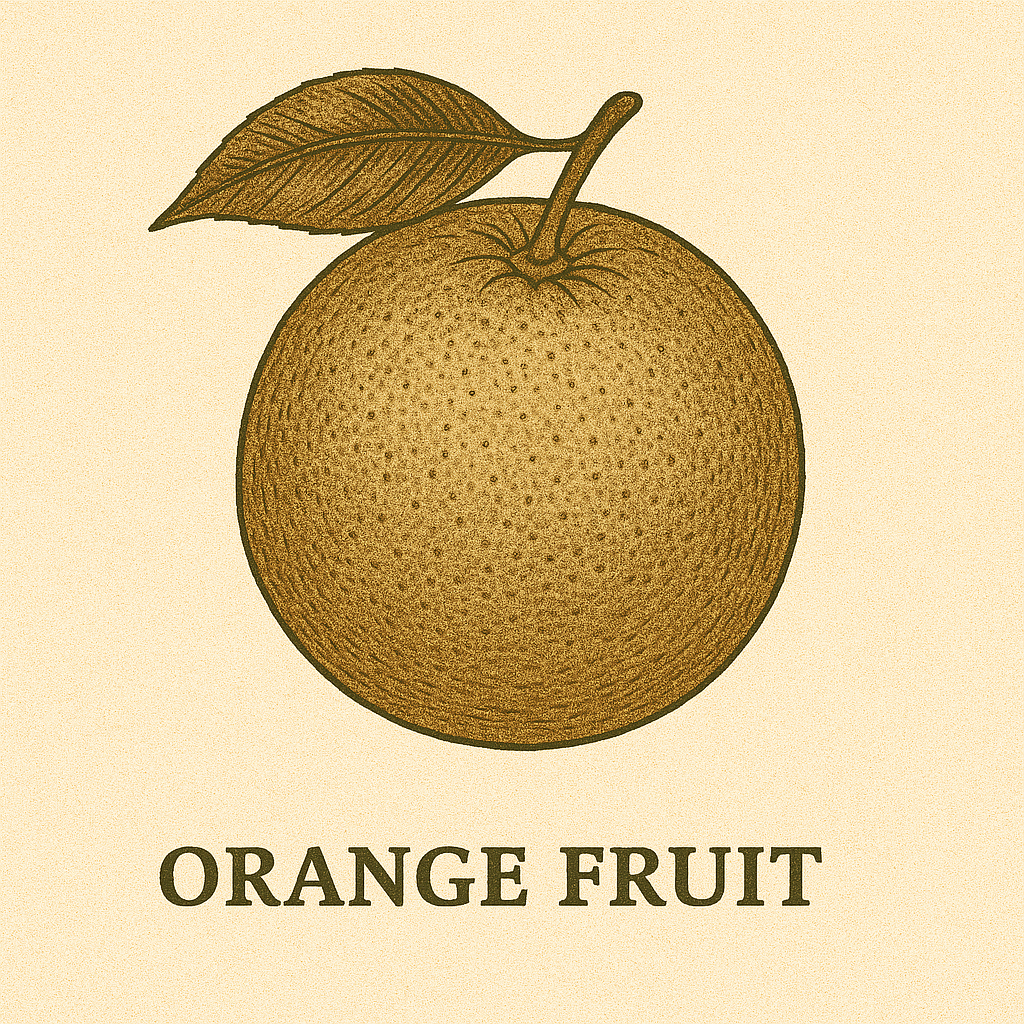
Key features:
- Has a thick peel
- Contains seeds and juice vesicles
- Develops from the ovary of a flower
Use in Biology Practical: You may be asked to draw the section of an orange or identify fruit parts like pericarp and locules.
Specimen K – Honey Bee
Honey bees are social insects known for making honey and pollinating flowers.

Key features:
- Has a stinger
- Divided into three parts (head, thorax, abdomen)
- Lives in colonies with a queen, workers, and drones
Use in Biology Practical: You may be asked to describe the bee’s structure or its role in pollination.
Specimen L – Land Snail
Land snails are slow-moving animals with soft bodies and a spiral shell.
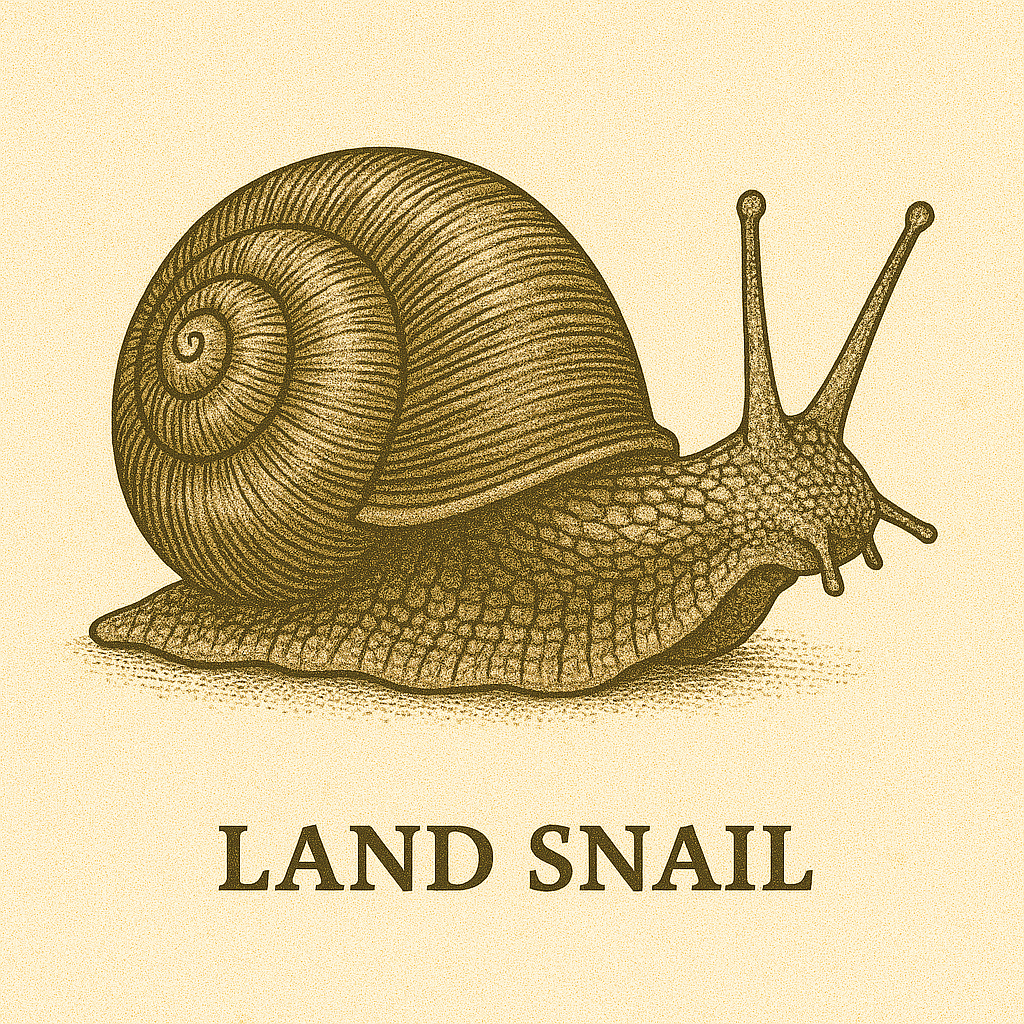

Key features:
- Has a coiled shell
- Has a muscular foot for movement
- Has tentacles with eyes at the tips
Use in Biology Practical: You may be asked to draw the snail and label the parts or explain how it moves.
Specimen M – Guava Fruit
Guava is a fleshy fruit with small seeds inside. It is rich in nutrients and has a sweet taste.

Key features:
- Green outer skin
- Contains many seeds inside
- Formed from the ovary of a flower
Use in Biology Practical: You may be asked to describe the fruit structure and identify it as a simple fleshy fruit.
Specimen N – Irish Potato Tuber
Irish potato is a type of underground stem called a tuber. It stores food.

Key features:
- Contains eyes or buds
- Rich in starch
- Can grow into a new plant
Use in Biology Practical: You may be asked to draw and label the potato and explain how it reproduces asexually.
Specimen O – Sweet Potato Tuber
Sweet potato is also a tuber, but unlike Irish potato, it is a root tuber, not a stem.

Key features:
- Stores food in roots
- Does not have eyes like Irish potato
- Can also be used to grow new plants
Use in Biology Practical: You may be asked to compare it with the Irish potato and state the difference between stem and root tubers.
These specimens cover a wide range of Biology topics such as:
- Insects and Arthropods (e.g., Housefly, Butterfly, Grasshopper)
- Fruits and Seeds (e.g., Orange, Guava, Bean Seed)
- Animal Bones and Structures (e.g., Rabbit Humerus and Femur)
- Other Organisms (e.g., Spider, Land Snail, Crayfish)
You should study the characteristics and uses of each specimen. Be ready to answer questions like:
- How do you identify this specimen?
- What is its function in nature?
- Which group (class, phylum, etc.) does it belong to?
- What are the labelled parts?
Also, practice drawing neat diagrams and labeling correctly, as this can earn you a lot of marks.
What If the School Can’t Provide All the Specimens?
NECO understands that not every school may be able to give each student all 15 specimens. In such cases, NECO allows schools to group students, with one full set of specimens shared by 10 students.
So, if you don’t have all the specimens in front of you, don’t panic. Just make sure you observe carefully and write the correct answers based on what is provided.
Important Notes for Teachers – Teacher’s Report
Teachers who are supervising the Biology Practical must fill out a special Teacher’s Report Form. This form must be placed inside the envelope containing the students’ answer scripts. The report helps NECO understand how the exam went in each center.
Here’s what the teacher must do on the form:
- Write down the types of specimens provided
- Mention any challenges in getting the specimens
- Note any problem faced by individual students during the exam
This report is very important and must not be forgotten.
How to Prepare as a Student
Here are a few tips to help you prepare for the Biology Practical exam:
- Study the specimens listed above and know how to identify each one.
- Watch videos or see real-life samples of each specimen if possible.
- Practice how to draw and label neatly using your pencil and ruler.
- Learn basic biology terms related to the specimens like types of reproduction, parts of a flower, types of fruit, etc.
- Ask your teacher for help if you don’t understand any part.
Final Words
The NECO 2025 Biology Practical is nothing to fear if you prepare well. Use this guide to start your preparation. Learn how to observe and describe the specimens clearly. Practice drawing and improve your labeling.
On the exam day, stay calm and focused. Follow instructions, and give your best. With good preparation and the right mindset, success is sure.
We wish you all the best in your NECO Biology Practical!

