NECO Geography OBJ 2025
01-10: BBEABCAEDB
11-20: DBEBDACBED
21-30: ACAEBBEEBE
31-40: AADAEDEBAC
41-50: ABDBCCDAAA
51-60: ADADCABDCE
COMPLETED!!!
NECO Geography (Practical / Physical) 2025
Number 1

==================
Number 2
(2a)

-In a solar eclipse, the Moon casts its shadow on Earth, blocking sunlight partially or fully.
-In a lunar eclipse, Earth’s shadow falls on the Moon, causing it to darken or turn reddish.
These differences illustrate the relative positions and observational effects of the two eclipses
(2b)
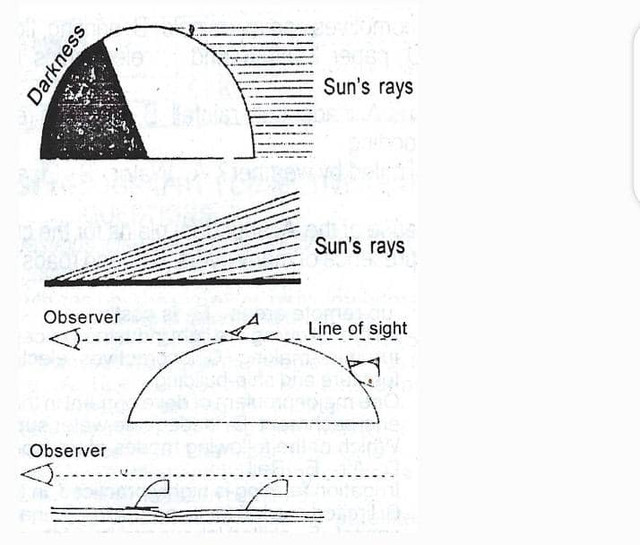
The varying times of sunrise and sunset around the world demonstrate Earth’s spherical shape and rotation.
==================
Number 3
(3a)
(i) Granite
(ii) Basalt
(iii) Diorite
(3b)
(i) Crystalline Texture:
Igneous rocks are generally crystalline in nature, with interlocking mineral grains. The size of the crystals depends on the rate of cooling—slow cooling forms large crystals (e.g., granite), while rapid cooling forms small or no crystals (e.g., basalt).
(ii) Hardness and Durability:
These rocks are usually very hard and resistant to weathering and erosion. This is because they are formed under high temperatures and pressures, making them compact and solid.
(iii) Lack of Fossils:
Igneous rocks do not contain fossils because the high temperatures of magma or lava would destroy any organic matter. Hence, they are not fossil-bearing rocks like some sedimentary rocks.
(3c)
(i) Construction Material: Rocks like granite and limestone are used for building houses, bridges, and roads.
(ii) Source of Minerals: Rocks contain valuable minerals like gold, copper, and iron which are mined for industrial use.
(iii) Agricultural Use: Some rocks, when weathered, form fertile soils useful for farming (e.g., basalt-derived soil).
(iv) Energy Source: Sedimentary rocks like shale may contain fossil fuels such as oil, coal, and natural gas.
==================
Number 4
(4a)
(i) Annual Temperature
Mean Annual: Temperature = (Sum of monthly temperatures) / Number of months
= (27 + 27 + 28 + 28 + 28 + 28 + 27 + 27 + 27 + 27 + 26 + 28) / 12
= 328 / 12
= 27.33°C
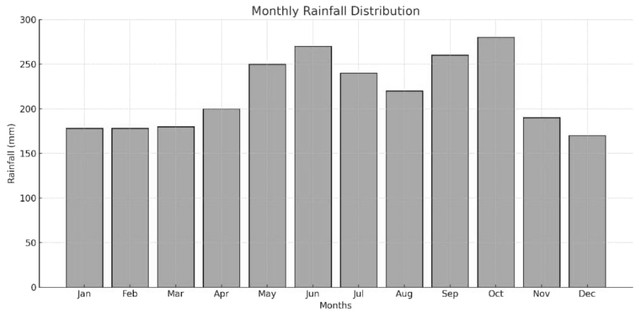
(ii) Mean Annual Rainfall:
Mean Annual Rainfall = (Sum of monthly rainfall) / Number of months
= (178 + 178 + 180 + 200 + 250 + 270 + 240 + 220 + 260 + 280 + 190 + 170) / 12
= 2616 / 12
= 218 mm
(iii) Rainfall Range:
Rainfall Range = Highest monthly rainfall – Lowest monthly rainfall
= 280 mm (October) – 170 mm (December)
= 110 mm
(4b)
DRAW THE DIAGRAM
==================
Number 5
(5a)
A Karst region is a landscape formed primarily by the chemical weathering (solution) of soluble rocks such as limestone and dolomite, resulting in distinctive landforms like sinkholes, caves, and underground streams.
(5b)
(i) Caves
(ii) Stalactites
(iii) Stalagmites
(iv) Underground rivers
(v) Dolines
(5c)
(i) Water supply: Provides underground water from springs and aquifers.
(ii) Tourism: Attracts visitors with caves and limestone formations.
(iii) Limestone mining: Supplies raw material for cement and construction.
(iv) Research: Useful for geological and environmental studies.
(5d)
(i) Water pollution
(ii) Ground subsidence
(iii) Limited agriculture
(iv) Accessibility issues
(v) Water scarcity
==================
Number 6
(6a)
Environmental balance refers to a state of stability and harmony among living organisms (plants, animals, humans) and their physical environment (air, water, soil), where natural processes occur without serious disruption. It ensures sustainable interaction among components of the ecosystem, allowing life to thrive without degradation.
(6b)
(i) Afforestation and Reforestation: Planting trees to restore lost vegetation and improve air quality.
(ii)Proper Waste Management: Recycling and disposing of waste responsibly to prevent pollution.
(iii) Controlled Use of Natural Resources: Using water, minerals, and energy efficiently to avoid depletion.
(iv) Environmental Education and Awareness: Teaching people to adopt eco-friendly habits and conservation practices.
(6c)
(i) Loss of Soil Fertility:
Erosion removes the topsoil, which contains essential nutrients needed for plant growth. This leads to poor crop yields and reduced agricultural productivity, affecting food supply and biodiversity.
(ii) Habitat Destruction:
Erosion can degrade or wash away habitats such as riverbanks, forests, and wetlands. This threatens the survival of plant and animal species, disrupts ecological balance, and may lead to species migration or extinction.
==================
Number 8
(8a)
(i) Satellite Imagery
(ii) Aerial Photography
(iii) Field Surveys
(iv) Government or Institutional Records
(8b)
(i) Crime Mapping and Hotspot Analysis:
GIS helps law enforcement agencies identify crime-prone areas by mapping the locations, types, and frequency of crimes. This allows security forces to allocate resources more effectively and implement targeted patrols in high-risk zones.
(ii) Surveillance and Monitoring:
With real-time data from satellites and drones integrated into GIS, security agencies can monitor movement patterns, detect unusual activities, and track armed groups or bandits across regions, especially in remote or forested areas.
(iii) Disaster and Emergency Response Planning:
GIS assists in planning emergency response during security crises such as insurgent attacks or communal clashes. It helps in mapping safe evacuation routes, locating displaced persons, and coordinating rescue operations through spatial analysis.
==================
COMPLETED!!!
